Keeping your home Wi-Fi safe is a big worry for many. Mac Address Filtering can be a helpful tool. This article will show you how to use it to protect your network. Let’s get started.
Key Takeaways
- MAC address filtering lets you control who can use your Wi-Fi by allowing or blocking devices based on a unique code.
- Setting it up is done in the router’s settings by adding device codes to an allow or deny list.
- It boosts security but might be hard to manage with many devices and could cause issues with some.
- Works well for both home and business networks, letting only approved devices connect.
- You may need to update allowed device lists often as new devices join or leave the network.
Understanding MAC Address Filtering
MAC Address Filtering allows you to decide which devices can connect to your network based on their unique MAC addresses. By configuring your router’s settings, you can enable or disable MAC filtering as an additional layer of security.
Definition and Function
A MAC address is a unique number given to every device on a computer network. This number helps routers and other network devices know where to send data. MAC filtering uses these numbers to control access to a network.
It allows or blocks devices based on their MAC address.
MAC filtering adds an extra layer of security by controlling which devices can connect to your network.
With this method, admins make lists of allowed (whitelist) or denied (blacklist) addresses in the router’s settings. This way, only approved devices can access the wifi, helping prevent unauthorized users from getting in.
How to Implement
Setting up MAC address filtering boosts network security by controlling who can access your network. This guide outlines steps to implement it effectively on your wireless router.
- Log in to your router. Use a web browser and enter the IP address of your router. Often, this is “192.168.1.1” or “192.168.0.1” or “10.0.0.1”. You’ll need the admin password.

- Find the MAC filtering section. Look for “MAC Filtering”, “Access Control”, or something similar under settings.
- Enable MAC filtering. There should be an option to turn it on or off.
- Add devices to your allow list or deny list based on their unique MAC addresses.
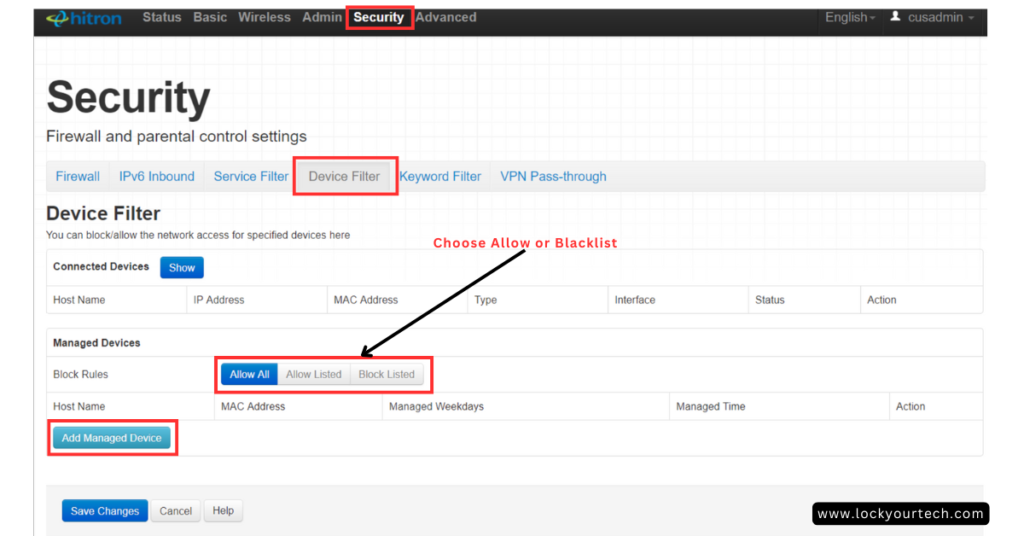
- Gather MAC addresses from devices you want to connect to your network; these are usually found in device settings, product boxes or by using a command prompt with commands like “ipconfig /all” for Windows or “ifconfig” for Mac and Linux systems.
- Enter each MAC address into the router’s allow list; this tells your router which devices can connect.
- Choose between allowing all except listed (blacklist) or denying all except listed (whitelist) for greater control over network access.
- Apply or save changes to ensure your settings take effect immediately.
Having used these steps myself, I found that setting up took less than 30 minutes but greatly improved my home network’s security against unauthorized access attempts, offering peace of mind knowing only my permitted devices could connect.
Benefits and Limitations of MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering adds an extra layer of security to your network by allowing only specified devices to connect, thus reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential threats.
It can, however, pose limitations as it may require significant management efforts when adding or removing devices from the approved list and could potentially lead to compatibility issues with certain devices.
Enhanced Network Security
MAC filtering in computer networks boosts security. This method stops unapproved devices from connecting to the network. It checks the MAC addresses of devices trying to access the network.
Only those on a list can get in. This keeps hackers out. They often use unknown MAC addresses.
This feature is key in both home and business networks. It makes sure only trusted devices connect. With MAC address filtering, network admins have control over which devices join their networks.
This lowers risks like data theft and unauthorized access.
Potential Compatibility Issues
After implementing MAC address filtering on your network for enhanced security, you may encounter potential compatibility issues. Certain devices, especially older ones or those from different manufacturers, might not fully support MAC address filtering.
This can lead to these devices being unable to connect to the network despite having legitimate access. Furthermore, managing a large number of authorized MAC addresses can be challenging and time-consuming, especially as the number of connected devices increases.
It’s vital to recognize that some networking equipment from various vendors may have different approaches to MAC address filtering which could cause interoperability issues when used together.
These variations in implementation might result in certain features or settings not working as expected across all devices within the network, leading to inconsistencies and complications in managing device access.
Related: 10 Must-Follow Steps to Secure Your Home Network
Practical Applications
Practical Applications of MAC address filtering can be seen in home networks and business networks. It allows for specific devices to gain access, preventing unauthorized entry while ensuring a secure network environment.
Home Networks
Home networks can benefit from MAC address filtering as a security method. This allows only authorized devices to access the network, preventing unauthorized access. By creating a list of approved MAC addresses, you can control which devices connect to your home network.
This adds an extra layer of protection against potential security threats.
When setting up MAC address filtering for your home network, you’ll be able to log into the router’s settings and navigate to the advanced options. From there, you can configure the filtering by inputting the MAC addresses of the authorized devices.
This process ensures that only specified devices are allowed to connect while denying access to others.
Business Networks
Business networks use MAC address filtering for enhanced security. This method allows businesses to control which devices can access the network based on their MAC addresses. By maintaining a list of authorized MAC addresses, businesses prevent unauthorized access and potential security threats to their network interface controllers.
Moreover, this approach is particularly beneficial for businesses that require stringent control over the devices connected to their network.
Conclusion
Mastering MAC Address Filtering can greatly improve your network’s security and manage access to specific devices. By understanding its advantages and limitations, you can make informed choices for both home and business networks.
Implementing MAC filtering as part of your network’s security strategy is a proactive step towards safeguarding your system from unauthorized access.
Considering the practical applications, such as preventing unauthorized access and improving network management, mastering MAC Address Filtering is essential in today’s constantly changing world of computer security.
In conclusion, by examining the various aspects of MAC Filter and MAC Address Filter, you’ll be better prepared to use this powerful tool effectively within your network.
FAQs
1. What is MAC address filtering?
MAC, or Media Access Control, address filtering is a security measure that allows or blocks devices based on their MAC addresses. It’s an access control method used in network management for authentication and to prevent unauthorized access.
2. How does MAC address filtering work?
When MAC filtering is enabled on your router, it checks the physical address of each device trying to connect to the network. If the device’s MAC address matches one on the allowed list (whitelist), it gets access; if it’s on the blacklist, it’s denied access.
3. Can I disable MAC address filter?
Yes, you can disable this feature from your router settings usually found under ‘Advanced’ options or similar depending upon your specific hardware like Netgear or others.
4. Are there any disadvantages of using Mac Filtering?
While providing an extra layer of security by allowing only certain computers’ access points onto your wireless network, Mac Filtering may be bypassed through a process called “MAC spoofing”. This happens when hackers mimic legitimate identifiers (MAC addresses) to gain unauthorized entry.
5. Is every device assigned unique MAC Address?
Yes, every network card in smartphones and other devices has a unique hexadecimal number assigned as its MAC Address which serves as its identifier while connecting to internet networks via Wi-Fi Protected Access systems among others.
6. Does enabling Mac Filtering guarantee complete Network Security?
No! While beneficial for controlling who accesses your local area network (LAN), relying solely on mac authentication isn’t foolproof against sophisticated attacks like Denial-of-Service attack and cannot replace multi-factor authentication measures.